Kubeflow
- Kubeflow Charmers | bundle
- Cloud
| Channel | Revision | Published |
|---|---|---|
| latest/candidate | 294 | 24 Jan 2022 |
| latest/beta | 430 | 30 Aug 2024 |
| latest/edge | 423 | 26 Jul 2024 |
| 1.10/stable | 436 | 07 Apr 2025 |
| 1.10/candidate | 434 | 02 Apr 2025 |
| 1.10/beta | 433 | 24 Mar 2025 |
| 1.9/stable | 432 | 03 Dec 2024 |
| 1.9/beta | 420 | 19 Jul 2024 |
| 1.9/edge | 431 | 03 Dec 2024 |
| 1.8/stable | 414 | 22 Nov 2023 |
| 1.8/beta | 411 | 22 Nov 2023 |
| 1.8/edge | 413 | 22 Nov 2023 |
| 1.7/stable | 409 | 27 Oct 2023 |
| 1.7/beta | 408 | 27 Oct 2023 |
| 1.7/edge | 407 | 27 Oct 2023 |
juju deploy kubeflow --channel 1.10/stable
Deploy Kubernetes operators easily with Juju, the Universal Operator Lifecycle Manager. Need a Kubernetes cluster? Install MicroK8s to create a full CNCF-certified Kubernetes system in under 60 seconds.
Platform:
This guide describes how to install Charmed Kubeflow (CKF) behind a web proxy.
Prepare your environment
Before installing CKF, first you need to set up your client with the required proxy settings.
Configure snap
Save the value of your proxy server address for reuse:
PROXY=http://<username>:<password>@<proxy IP>:<proxy port>/
The proxy IP and port are usually given by your network administrator.
Add the username:<password>@ part only if the proxy server is configured with credentials, check with your network administrator.
Set the snap proxy settings:
sudo snap set system proxy.http=$PROXY
sudo snap set system proxy.https=$PROXY
This will enable you to install snap packages.
Now restart the snap service:
sudo systemctl restart snapd.service
Configure MicroK8s
Install Microk8s:
sudo snap install microk8s --classic --channel=1.29-strict/stable
Add the current user to the Microk8s group:
sudo usermod -a -G snap_microk8s $USER
newgrp snap_microk8s
This way you don’t have to use sudo for every Microk8s command.
Enable microk8s add-ons needed to run Charmed Kubeflow.
Note that the metallb range can change depending on the use case and the environment:
sudo microk8s enable dns:$(resolvectl status | grep "Current DNS Server" | awk '{print $NF}') # This sets the dns to your current nameserver
sudo microk8s enable storage ingress metallb:10.64.140.43-10.64.140.49
Get the value cluster-cidr, stored in /var/snap/microk8s/current/args/kube-proxy, and save it in a variable:
cat /var/snap/microk8s/current/args/kube-proxy | grep cluster-cidr
You should see an output similar to this:
--cluster-cidr=<cluster cidr> # save this value
CLUSTER_CIDR=<cluster cidr>
Repeat the process with service-cluster-ip-range, stored in /var/snap/microk8s/current/args/kube-apiserver:
cat /var/snap/microk8s/current/args/kube-apiserver | grep service-cluster-ip-range
You should see an output similar to this:
-service-cluster-ip-range=<service cluster ip range> # save this value
SERVICE_CIDR=<service cluster ip range>
You will need these two values in the next step and later when installing Juju.
See MicroK8s | Installing behind a proxy for more details.
Get the Internal IP of the nodes where your cluster is running. You can check that by running:
microk8s kubectl get nodes -o wide
Take note of the INTERNAL-IP value.
Save the IP(s) in a variable with suffix /24, comma-separated if you have a multi-node cluster.
NODE_IP=<nodes internal ip(s)>/24
Set the proxy settings in containerd-env. Modify the containerd-env file located in ${SNAP_DATA}/args/containerd-env (normally /var/snap/microk8s/current/args/containerd-env):
HTTPS_PROXY=http://<username>:<password>@<proxy IP>:<proxy port>/
NO_PROXY=<cluster-cidr>,<service-cluster-ip-range>,<nodes internal ip(s)>/24,127.0.0.1
Restart the microk8s snap to pick up the changes:
sudo snap restart microk8s
Check that Microk8s is running with the desired add-ons:
microk8s status
You should see an output similar to this:
microk8s is running
high-availability: no
datastore master nodes: 127.0.0.1:19001
datastore standby nodes: none
addons:
enabled:
dns # (core) CoreDNS
ha-cluster # (core) Configure high availability on the current node
hostpath-storage # (core) Storage class; allocates storage from host directory
ingress # (core) Ingress controller for external access
metallb # (core) Loadbalancer for your Kubernetes cluster
storage # (core) Alias to hostpath-storage add-on, deprecated
Configure Juju
Export the system proxy settings used by the Juju client. Make sure to set metallb as you configured it when installing Microk8s.
Make sure to replace <hostname> with your own hostname.
export http_proxy=$PROXY
export https_proxy=$PROXY
export no_proxy=$CLUSTER_CIDR,\
$SERVICE_CIDR\
127.0.0.1,\
$NODE_IP,\
<hostname>,\
.svc,\
.local,\
10.64.140.0/24,\ # This is the metallb IP range
.nip.io
Install Juju
sudo snap install juju --classic --channel=3.4/stable
Create a Juju controller in your Microk8s cluster and set the proxy model default values. Change metallb if you configured it differently.
juju bootstrap microk8s uk8s --model-default juju-http-proxy=$http_proxy \
--model-default juju-https-proxy=$https_proxy \
--model-default juju-no-proxy=$no_proxy
Add Juju model
juju add-model kubeflow
Make sure Kubeflow model has your proxy settings, run:
juju model-config
You should see the proxy settings in the juju-http-proxy, juju-https-proxy and juju-no-proxy variables.
Deploy CKF
To deploy CKF and access its dashboard, follow the steps provided in the general installation guide.
Use Kubeflow components behind a proxy
Notebooks
Apply the following PodDefault to your user namespace so each notebook you create will have proxy configurations set.
The NO_PROXY and no_proxy values would be the same as you configured in the Juju model.
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -n $USER_NAMESPACE -f -
apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1alpha1
kind: PodDefault
metadata:
name: notebook-proxy
spec:
desc: Add proxy settings
env:
- name: HTTP_PROXY
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: http_proxy
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: HTTPS_PROXY
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: https_proxy
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: NO_PROXY
value: <cluster cidr>,<service cluster ip range>,127.0.0.1,<nodes internal ip(s)>/24,<cluster hostname>,.svc,.local
- name: no_proxy
value: <cluster cidr>,<service cluster ip range>,127.0.0.1,<nodes internal ip(s)>/24,<cluster hostname>,.svc,.local,.kubeflow
selector:
matchLabels:
notebook-proxy: "true"
EOF
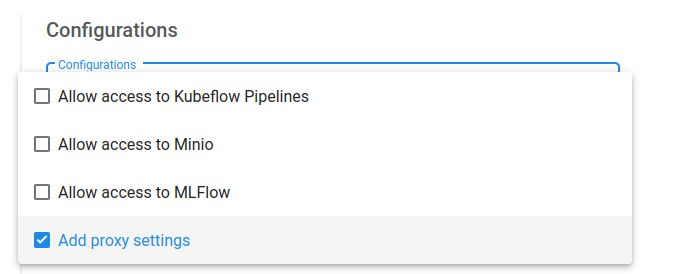
You should now be able to see Add proxy settings when creating a new notebook under Advanced Options > Configurations. Always select that option.
Katib
Before running a Katib experiment, add your proxy environment variables to your experiment definition for each container under spec.trialTemplate.trialSpec.spec.template.spec.containers:
env:
- name: HTTP_PROXY
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: http_proxy
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: HTTPS_PROXY
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
- name: https_proxy
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/ # replace with $PROXY
Expand to see full Katib experiment example
apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1beta1
kind: Experiment
metadata:
name: grid-proxy
spec:
objective:
type: maximize
goal: 0.99
objectiveMetricName: Validation-accuracy
additionalMetricNames:
- Train-accuracy
algorithm:
algorithmName: grid
parallelTrialCount: 1
maxTrialCount: 1
maxFailedTrialCount: 1
parameters:
- name: lr
parameterType: double
feasibleSpace:
min: "0.001"
max: "0.01"
step: "0.001"
- name: num-layers
parameterType: int
feasibleSpace:
min: "2"
max: "5"
- name: optimizer
parameterType: categorical
feasibleSpace:
list:
- sgd
- adam
- ftrl
trialTemplate:
primaryContainerName: training-container
trialParameters:
- name: learningRate
description: Learning rate for the training model
reference: lr
- name: numberLayers
description: Number of training model layers
reference: num-layers
- name: optimizer
description: Training model optimizer (sdg, adam or ftrl)
reference: optimizer
trialSpec:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
containers:
- name: training-container
image: docker.io/kubeflowkatib/mxnet-mnist:latest
command:
- "python3"
- "/opt/mxnet-mnist/mnist.py"
- "--batch-size=64"
- "--lr=${trialParameters.learningRate}"
- "--num-layers=${trialParameters.numberLayers}"
- "--optimizer=${trialParameters.optimizer}"
env:
- name: HTTP_PROXY
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/
- name: http_proxy
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/
- name: HTTPS_PROXY
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/
- name: https_proxy
value: http://10.0.1.119:3128/
restartPolicy: Never
Pipelines
If your pipeline needs to download data or pull an image, you can inject your proxy environment variables into a pipeline from inside a notebook with the KFP SDK as done in this example notebook.
Istio
If needed, configure proxy settings for Istio as follows:
kubectl apply -n kubeflow -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: proxy
spec:
hosts:
- my-company-proxy.com # ignored
addresses:
- 10.0.1.119/32 # replace with proxy IP
ports:
- number: 3128 # replace with proxy port
name: tcp
protocol: TCP
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
EOF