Identity Platform
- Identity Charmers | bundle
| Channel | Revision | Published |
|---|---|---|
| latest/edge | 39 | 14 Jan 2025 |
| istio/edge | 38 | 12 Jan 2025 |
| 0.3/edge | 32 | 20 Sep 2024 |
| 0.2/edge | 25 | 09 May 2024 |
| 0.1/edge | 17 | 25 Apr 2024 |
juju deploy identity-platform --channel edge
Deploy Kubernetes operators easily with Juju, the Universal Operator Lifecycle Manager. Need a Kubernetes cluster? Install MicroK8s to create a full CNCF-certified Kubernetes system in under 60 seconds.
Platform:
Architecture Overview
The Canonical Identity Platform is a comprehensive identity solution that serves two primary functions:
- Identity Provider: It acts as a standalone source of truth for user identities, allowing you to store and manage user credentials, profiles, and sessions directly within the platform. This native identity management is powered by Charmed Kratos.
- Identity Broker: It federates external identity providers (Microsoft Entra ID, Okta, Google, GitHub, etc.) to downstream service providers (Grafana, Kafka, and other workloads), creating a unified sign-on experience.
The diagram below illustrates the high-level architecture and dependencies of the solution:
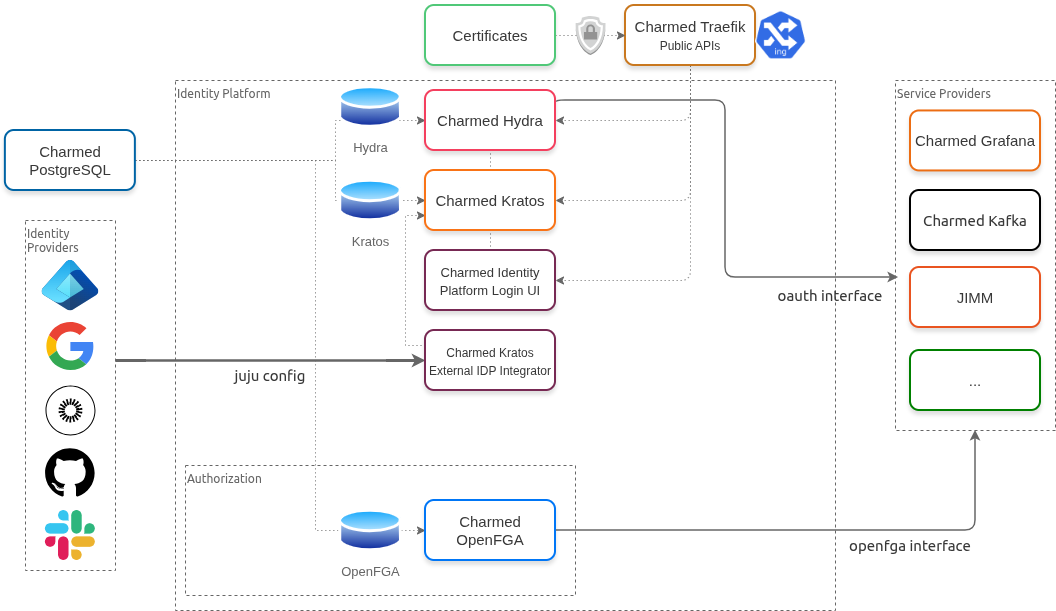
The Canonical Identity Platform orchestrates several interoperable charmed operators to deliver this functionality.
Core Components
The solution consists of the following modular components:
- Charmed Kratos – The core Identity Provider engine. It handles user management, registration, login flows, and secure storage of local credentials (passwords, MFA).
- Charmed Hydra – The OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) server. It acts as the secure interface for applications to authenticate users, regardless of whether the identity comes from Kratos (local) or an external provider.
- Charmed Identity Platform Login UI – The user interface for login, registration, settings, and account recovery screens.
- Charmed Kratos External IDP Integrator – A helper operator that facilitates the Identity Broker role by configuring Charmed Kratos to trust and exchange identities with external providers.
- Charmed OpenFGA (Optional) – An authorization engine based on Fine-Grained Authorization (FGA). It allows applications to define flexible permission models and offload complex access control logic from their code.
- Charmed PostgreSQL – The database provider for Kratos and Hydra.
- Charmed Traefik – Ingress for public-facing endpoints and internal admin APIs.
Integration Points
The Canonical Identity Platform leverages Juju relations and configs to simplify the integration of Single Sign-On (SSO) across your infrastructure. There are three main integration points:
-
oauthrelation interface: This is the standard interface for connecting applications (Service Providers) to the platform.- Charmed Applications: When you relate a charm to Charmed Hydra via
oauth, the platform automatically registers an OAuth client and manages its lifecycle. - External Workloads: Non-charmed applications that support OIDC can also be integrated using Charmed Hydra’s actions.
- Charmed Applications: When you relate a charm to Charmed Hydra via
-
openfgarelation interface: This interface connects applications to the Authorization engine.- Services can relate to Charmed OpenFGA to query permissions (e.g., “Can User A view Document B?”) and store relationship tuples, decoupling authorization logic from application code.
-
Kratos External IdP Integrator (via juju config): This interface manages the upstream connections when the platform acts as an identity broker.
- By deploying an instance of the Integrator charm and setting the
juju config, you can dynamically register external identity providers. - Multiple providers can be supported simultaneously by deploying multiple instances of the Integrator charm.
- By deploying an instance of the Integrator charm and setting the
Interested in learning how to integrate your application with the Canonical Identity Platform? Check our how-to guides.