MongoDB
- Canonical
- Databases
| Channel | Revision | Published | Runs on |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6/stable | 199 | 04 Oct 2024 | |
| 6/candidate | 199 | 04 Oct 2024 | |
| 6/beta | 199 | 04 Oct 2024 | |
| 6/edge | 204 | 12 Nov 2024 | |
| 5/stable | 117 | 20 Apr 2023 | |
| 5/candidate | 117 | 20 Apr 2023 | |
| 5/edge | 139 | 21 Nov 2023 | |
| 5/edge | 109 | 06 Mar 2023 | |
| 3.6/stable | 100 | 28 Apr 2023 | |
| 3.6/candidate | 100 | 13 Apr 2023 | |
| 3.6/edge | 100 | 03 Feb 2023 |
juju deploy mongodb --channel 6/edge
Deploy universal operators easily with Juju, the Universal Operator Lifecycle Manager.
Platform:
Sharding in Charmed MongoDB
This page goes over the logic and implementation behind sharding in Charmed MongoDB. For information about how sharding works in general, we recommend checking out this page from MongoDB’s official documentation: MongoDB | Sharding in MongoDB.
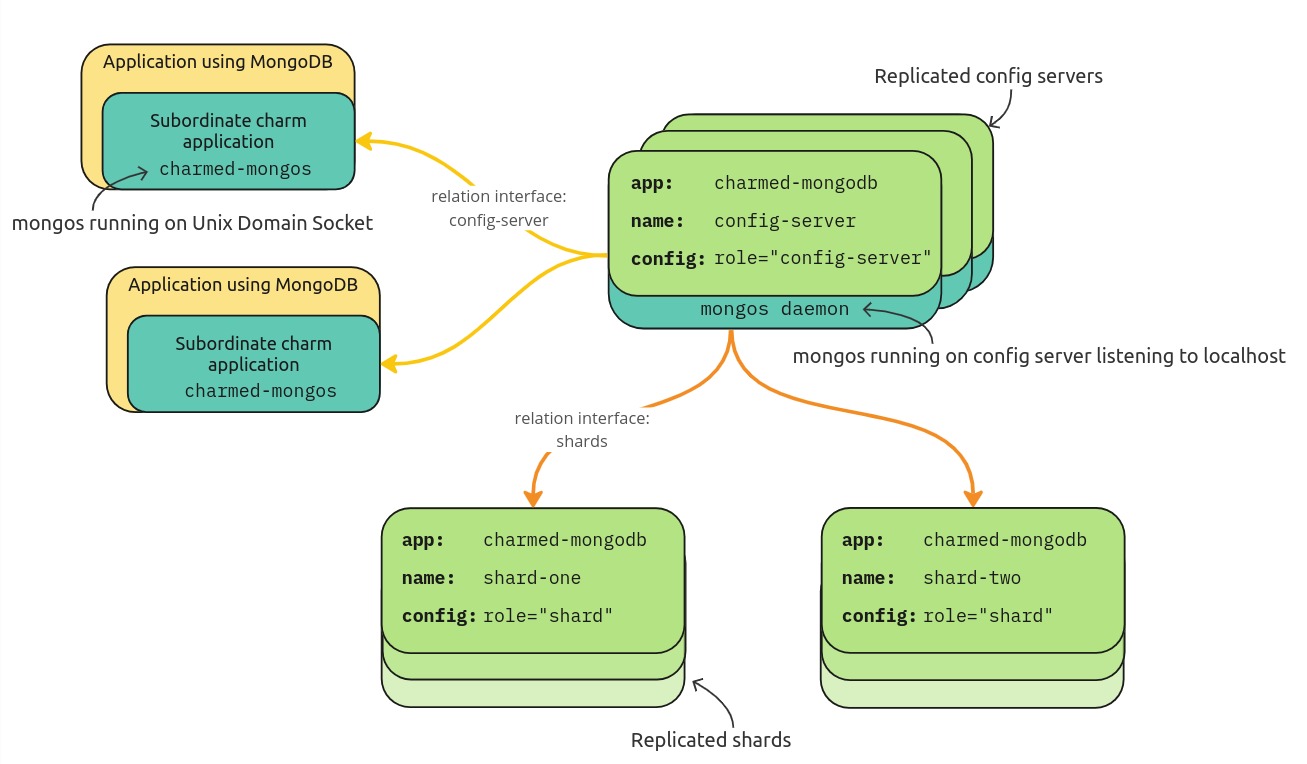
In Charmed MongoDB, sharding is designed around the idea of multiple juju applications making up the cluster, unlike replication, where multiple units make up the replica set. These different applications act as cluster components such as shards, config-servers, and mongos-routers. In this page, we will describe these components and the charms they are associated with.
Summary
- Sharded cluster components
config-servershardmongos
- Sharded cluster architecture
- Replication-only vs. sharded cluster deployments
Sharded cluster components
config-server
config-servers exist as a configuration of the already existing Charmed MongoDB charm. The config server manages the related sharding applications and is responsible for adding/removing shards, creating users, managing passwords, creating backups, and enabling TLS.
shard
Shards exist as a configuration of the already existing Charmed MongoDB charm. Once deployed as a shard, shards are unable to create users, manage passwords, and create backups.
mongos
The mongos router is present in two forms in Charmed MongoDB:
- Cluster admin - In this case,
mongosruns as an administrative daemon within the config-server, managing shards, users, passwords, etc. It is not advisable to access thismongosdaemon directly in a production environment. - Router for client connections - In this case,
mongosruns as a subordinate charm, Charmed Mongos, and acts as an independent router for client applications.
Designed for reduced latency
We designed our deployments around creating the most efficient sharded cluster possible. For this reason, the administrative mongos router runs within the same virtual machine as the config-server. This means that administrative cluster actions do not need to make additional network calls to configure the cluster.
On the subordinate Mongos charm, a similar approach is taken for the non-administrative mongos router (i.e. the mongos client router). In this case, mongos is running using the Unix Domain Socket so that client requests to the sharded cluster do not have to make a network call when interfacing with their associated router.
Sharded cluster architecture
The image below depicts an example deployment of a sharded cluster in Charmed MongoDB and the relationships between all components:
For more information about Charmed MongoDB sharded cluster deployments, check the following pages in this documentation:
- Tutorial > Deploy a sharded cluster > 2. Deploy MongoDB for beginner-friendly, guided steps
- How-To > Deploy MongoDB for concise instructions
Replication-only vs. sharded cluster deployments
Some key differences between a bare replica set deployment and a sharded cluster deployment include:
| Replication-only | Sharded cluster |
|---|---|
| Requires one MongoDB application | Requires multiple MongoDB applications |
Can create users via mongodb_client interface |
Can create users via config-server interface |
| Can be integrated with legacy interface | Cannot be integrated with legacy interface |