MicroK8s
- Canonical Kubernetes
| Channel | Revision | Published | Runs on |
|---|---|---|---|
| latest/edge | 242 | 02 Dec 2024 | |
| latest/edge | 241 | 02 Dec 2024 | |
| latest/edge | 240 | 02 Dec 2024 | |
| latest/edge | 239 | 02 Dec 2024 | |
| latest/edge | 238 | 02 Dec 2024 | |
| latest/edge | 237 | 02 Dec 2024 | |
| legacy/stable | 124 | 17 Aug 2023 | |
| legacy/stable | 121 | 17 Aug 2023 | |
| legacy/edge | 124 | 10 Aug 2023 | |
| legacy/edge | 125 | 10 Aug 2023 | |
| legacy/edge | 123 | 10 Aug 2023 | |
| legacy/edge | 122 | 10 Aug 2023 | |
| legacy/edge | 121 | 10 Aug 2023 | |
| 1.28/stable | 213 | 20 Sep 2023 | |
| 1.28/edge | 218 | 19 Sep 2023 | |
| 1.28/edge | 217 | 19 Sep 2023 | |
| 1.28/edge | 216 | 19 Sep 2023 | |
| 1.28/edge | 215 | 19 Sep 2023 | |
| 1.28/edge | 213 | 19 Sep 2023 |
juju deploy microk8s --channel 1.28/stable
Deploy universal operators easily with Juju, the Universal Operator Lifecycle Manager.
Platform:
This guide describes how to integrate Charmed MicroK8s with the Canonical Observability Stack(COS) to gather metrics, logs, alerts and display dashboards for the MicroK8s cluster.
Requirements
- A running Charmed MicroK8s cluster
If you are planning to deploy COS on the cluster itself, then you also need to follow the “Deploy Kubernetes charms” guide to configure the MicroK8s cluster as a Juju cloud. For this guide, we will assume that this has already been done and the Juju cloud is named microk8s-cloud.
Deploy COS
NOTE: If you have already deployed COS and only need to integrate it with your MicroK8s cluster, skip to the next section.
First, we create a model and deploy MetalLB. MetalLB will provide a public IP address for Prometheus, Loki and Grafana. Please choose an address that is appropriate for your network, in this example we will use 10.42.42.42.
juju add-model metallb-system microk8s-cloud
juju deploy metallb --channel 1.28/stable --config iprange=10.42.42.42-10.42.42.42
Next, deploy COS using the cos-lite bundle:
juju add-model cos microk8s-cloud
juju deploy cos-lite --channel edge --trust
After cos-lite deployment is complete, the juju status output should look like this. Notice how the traefik application is using the LoadBalancer IP we configured:
Model Controller Cloud/Region Version SLA Timestamp
cos zs microk8s-cloud/localhost 3.1.5 unsupported 10:19:47+03:00
App Version Status Scale Charm Channel Rev Address Exposed Message
alertmanager 0.25.0 active 1 alertmanager-k8s edge 88 10.152.183.44 no
catalogue active 1 catalogue-k8s edge 25 10.152.183.101 no
grafana 9.2.1 active 1 grafana-k8s edge 92 10.152.183.245 no
loki 2.7.4 active 1 loki-k8s edge 97 10.152.183.88 no
prometheus 2.46.0 active 1 prometheus-k8s edge 148 10.152.183.233 no
traefik 2.10.4 active 1 traefik-k8s edge 151 10.42.42.42 no
Unit Workload Agent Address Ports Message
alertmanager/0* active idle 10.1.144.199
catalogue/0* active idle 10.1.17.130
grafana/0* active idle 10.1.144.200
loki/0* active idle 10.1.17.136
prometheus/0* active idle 10.1.144.201
traefik/0* active idle 10.1.17.135
Our next step is to create offers for the metrics, logs and dashboard endpoints. This will allow us to connect our MicroK8s cluster to COS:
juju offer prometheus:receive-remote-write prometheus
juju offer loki:logging loki
juju offer grafana:grafana-dashboard grafana
Note the endpoint names from the output, e.g.:
Application "prometheus" endpoints [receive-remote-write] available at "admin/cos.prometheus"
Application "loki" endpoints [logging] available at "admin/cos.loki"
Application "grafana" endpoints [grafana-dashboard] available at "admin/cos.grafana"
We will need these names to configure the cross-model relations in the next step.
Integrate MicroK8s with COS
We will now switch back to our main model:
juju switch microk8s
Next, consume the COS endpoints:
juju consume admin/cos.prometheus prometheus
juju consume admin/cos.loki loki
juju consume admin/cos.grafana grafana
Deploy grafana-agent and integrate it with our COS endpoints:
juju deploy grafana-agent --channel edge
juju integrate grafana-agent prometheus
juju integrate grafana-agent loki
juju integrate grafana-agent grafana
As a final step, integrate microk8s with the grafana-agent:
juju integrate microk8s grafana-agent
Wait for everything to settle, the output of juju status should eventually look like this:
Model Controller Cloud/Region Version SLA Timestamp
microk8s zs zerostack/KHY 3.1.5 unsupported 10:55:27+03:00
SAAS Status Store URL
grafana active zs admin/cos.grafana
loki active zs admin/cos.loki
prometheus active zs admin/cos.prometheus
App Version Status Scale Charm Channel Rev Exposed Message
grafana-agent active 3 grafana-agent edge 18 no
microk8s 1.28.1 active 3 microk8s 1.28/stable 213 yes node is ready
Unit Workload Agent Machine Public address Ports Message
microk8s/0 active idle 0 172.16.100.241 16443/tcp node is ready
grafana-agent/0* active idle 172.16.100.241
microk8s/1* active idle 1 172.16.100.189 16443/tcp node is ready
grafana-agent/2 active idle 172.16.100.189
microk8s/2 active idle 2 172.16.100.129 16443/tcp node is ready
grafana-agent/1 active idle 172.16.100.129
Machine State Address Inst id Base AZ Message
0 started 172.16.100.241 9e1e142a-4a5c-407a-9605-6fe0e8abad3c ubuntu@22.04 nova ACTIVE
1 started 172.16.100.189 1ad53578-e1e4-42f2-a337-ba4f17f4be38 ubuntu@22.04 nova ACTIVE
2 started 172.16.100.129 46d9e8fd-a47c-44aa-b43e-1490394f29bc ubuntu@22.04 nova ACTIVE
Explore Dashboards
Retrieve the Grafana admin password
JUJU_MODEL=cos juju run grafana/leader get-admin-password --wait
The output should include the admin password, as well as the URL where you can access Grafana:
admin-password: x6a798da56as321
url: http://10.42.42.42/cos-grafana
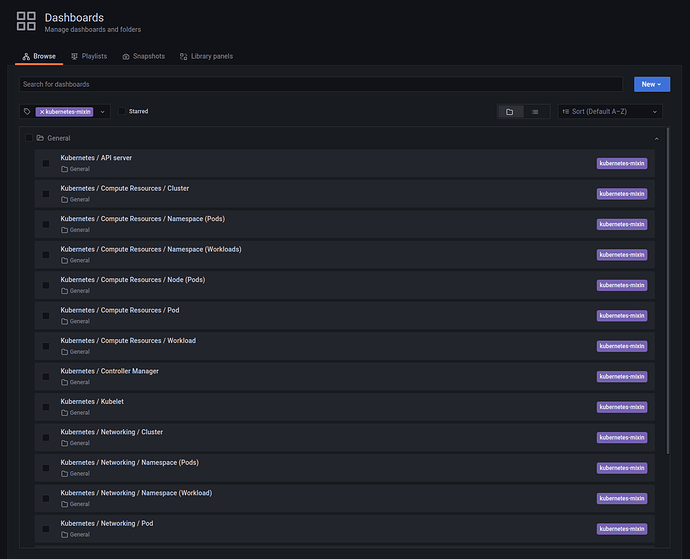
After logging in to Grafana, go to the list of Dashboards, and you can see a number of provisioned dashboards for the MicroK8s cluster:
Node Monitoring
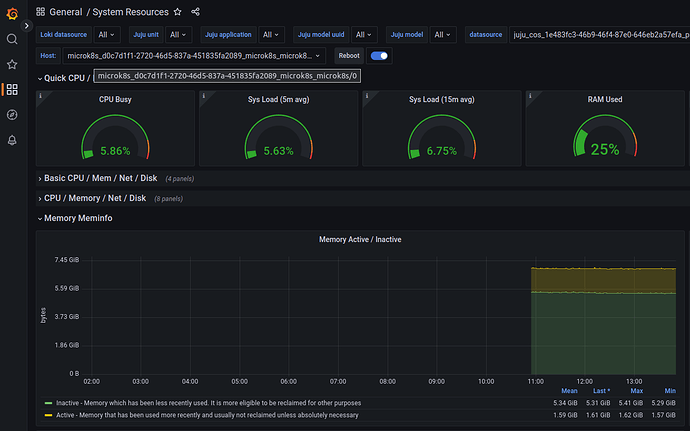
Use the General / System Resources dashboard to see metrics and graphs for the individual MicroK8s nodes:
An example view can be seen below:
Control Plane Services
The following dashboards can be used to monitor the respective control plane services of the MicroK8s cluster:
Kubernetes / API ServerKubernetes / KubeletKubernetes / ProxyKubernetes / SchedulerKubernetes / Controller Manager
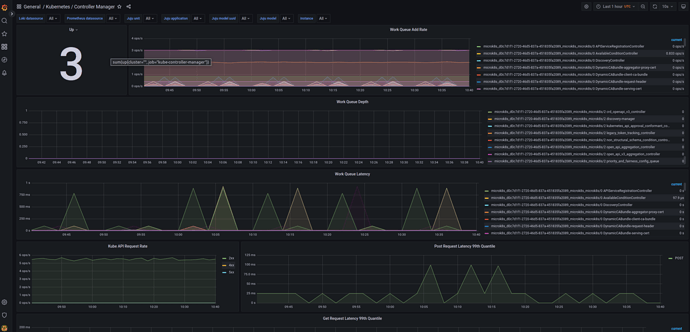
An example view of the Kubernetes / Controller Manager dashboard can be seen below:
Workload monitoring
The following dashboards can be used to monitor the status and compute usage of workloads running in the MicroK8s cluster:
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / ClusterKubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Pods)Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Workloads)Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Node (Pods)Kubernetes / Compute Resources / PodKubernetes / Compute Resources / Workload
The following dashboards can be used to monitor the networking traffic in the MicroK8s cluster:
Kubernetes / Networking / ClusterKubernetes / Networking / Namespace (Pods)Kubernetes / Networking / Namespace (Workloads)Kubernetes / Networking / PodKubernetes / Networking / Workload
The following dashboards can be used to monitor the status of PersistentVolumes in the MicroK8s cluster:
Kubernetes / Persistent Volumes
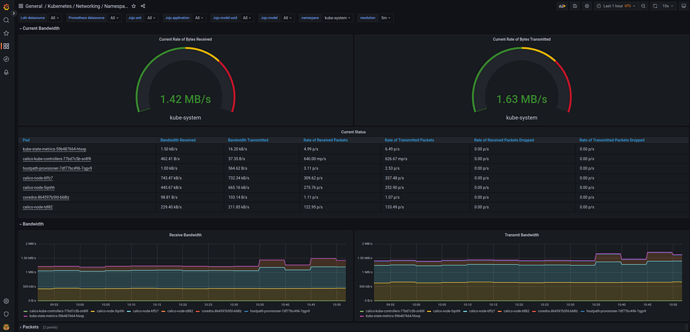
An example view of the Kubernetes / Networking / Namespace (Pods) dashboard can be seen below: